Outsourcing to Romania: Clear Guide & Top Tips for US Businesses
Outsource to Romania with confidence. Discover the benefits, costs, and practical steps for US businesses.

| This piece has been written in collaboration with Esther Friedberg Karp, an esteemed bookkeeper and QuickBooks ProAdvisor. |
|---|
Financial statements are an important part of understanding how a business is performing and the foundation underpinning growth planning.
Three key financial statements are used for monitoring: balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement.
Each of these statements will give you a different perspective on your business’s financial health and provide crucial insight into the state of the business.
This article breaks down everything you need to know about balance sheets, including the balance sheet formula, definition, and how to create a balance sheet.
| Table of contents |
|---|
The definition of a balance sheet is a financial statement that provides insight into a company’s financial position.
The balance sheet shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and net worth as of a specific date. You might also see net worth referred to as “equity” in a balance sheet.¹
The balance sheet looks at the balance of a company’s assets, liabilities, and net worth to understand whether the company has a negative or positive balance.
For publicly traded companies, it's a required financial statement for investors. It's part of the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), that companies use to measure and demonstrate financial results.²
The balance sheet equation, also known as the accounting equation, is actually a fairly simple one:
| Assets = Liabilities + Equity |
|---|
To understand the true value of a company’s assets, its equity and liabilities need to be added together.
Generally, balance sheets usually follow a standard format with assets on the left side and liabilities and equity added together on the right side.
Or, the assets are at the top and the liabilities and equity are added together underneath.
Let’s look at a balance sheet example to help make the concept clearer.
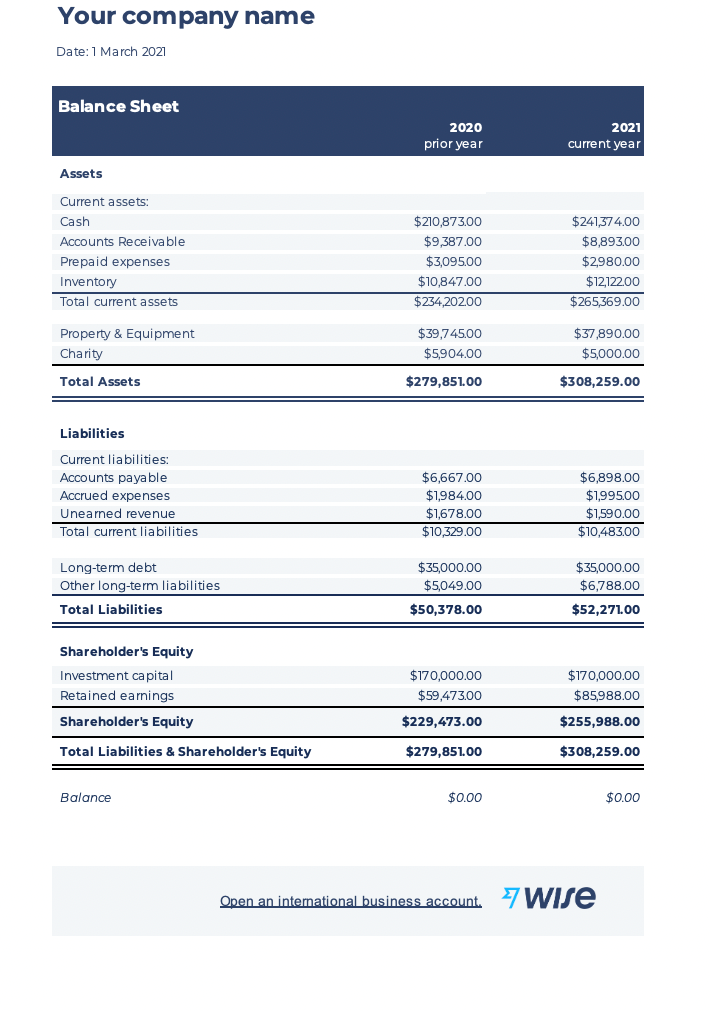
To better understand how a balance sheet is structured, here is an example from the Wise balance sheet template.
By entering the assets and liabilities plus shareholder equity, you can start to understand a company’s financial position better.
Comparing its equity plus liabilities helps you understand the true asset position of a company and the balance between the two.
Here is an example of a simple balance sheet
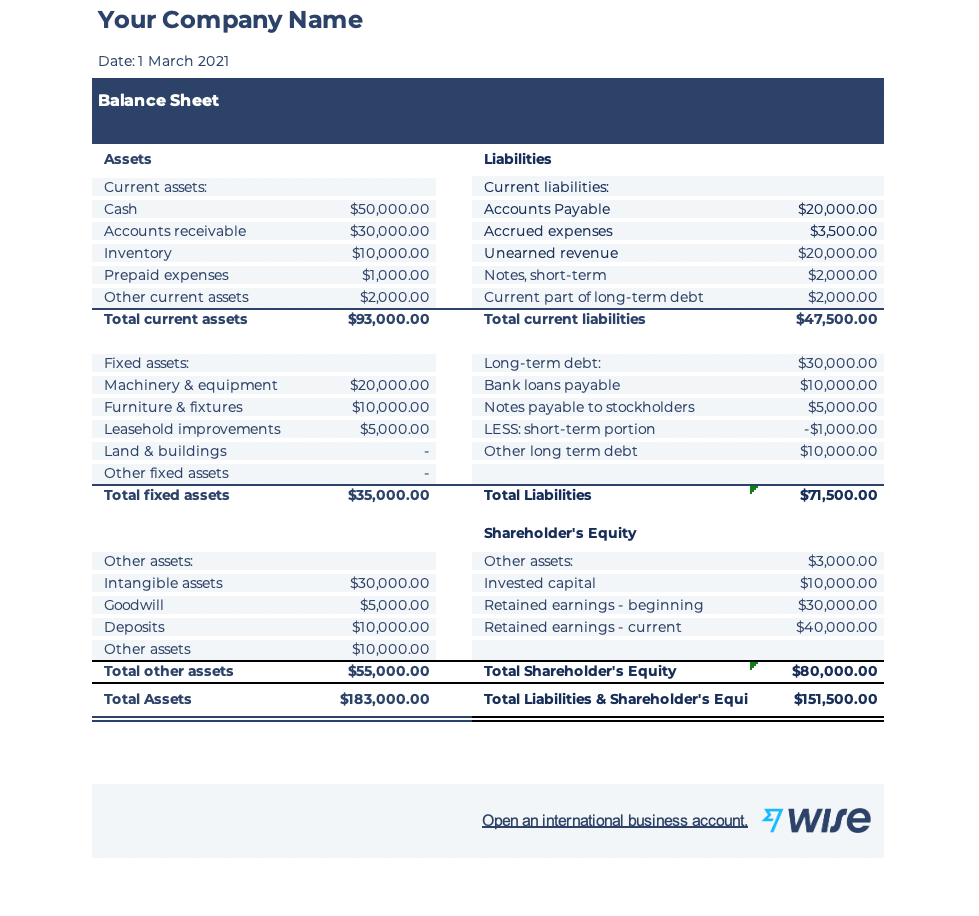
Here is an example of a comprehensive balance sheet
Get your free
Wise balance sheet template today
To structure a balance sheet, there are a few key pieces of information needed.
By breaking each section into line items, you can better understand the balance between cash and debt to ascertain business financial health.
The balance sheet shows your company’s debt versus its equity to determine the true value of assets held.
Once these are put together, the balance sheet will show a company’s assets.
Assets are defined as anything your business owns that has some kind of monetary value. That means that your business can easily sell or use these assets to make products or provide services.³
Assets are calculated differently depending on whether they are current or fixed assets, but the basic formula is to add up the value of cash and equivalents.
So let’s look at each one in more detail to understand how to calculate assets.
Current assets refer to cash and short-term investments or equivalents that a business can convert into cash within one year.
Current assets can include:
Fixed assets refer to long-term assets that a business owns, which are useful for more than one year.
Fixed assets can include:
Liabilities refer to debt obligations and loans that a business owes to other parties.
To calculate liabilities, you must identify all liabilities and debts of a business and add them together.
Liabilities include:
Similar to current assets, current liabilities refer to any debts or short-term financial obligations that a company must pay back within a year with cash.
These include Accounts payable and credit card balances.
Long-term liabilities are any debts or financial obligations that a company must pay with cash that are due more than a year later.
Equity on a balance sheet looks at the money that would be left over if a business sold all its assets and paid off its debts.
Equity can be calculated by subtracting the business’s liabilities from its assets.
Shareholder equity is calculated on the balance sheet by adding investment capital and accumulated retained earnings.
Equity will include:
Any capital that shareholders have invested in the company
Current earnings at the beginning of the year versus earnings now

On top of showing assets, liabilities, and equity, a balance sheet can help you across many business aspects.
1. Prepare your tax returns
A balance sheet is needed as part of your company’s financial statements for tax purposes.
In addition, a balance sheet is a core component of tax returns for businesses, as it supports what is being reported.
2. Monitor business health
Using a balance sheet, businesses gain better insight into financial health.
It helps you understand what your business owns versus what it owes, which can be useful for future financial planning.
A balance sheet is a vital tool for monitoring performance and creating business growth strategies for international businesses.
3. Secure funding sources
A balance sheet is necessary for businesses looking to apply for financing or bringing investors on board.
It’s a crucial financial statement that investors and third-party loan providers will ask for as part of their due diligence process.
4. Look at rates of return
Using financial statements such as a balance sheet, businesses understand how well they generate returns on capital invested in the company.
Companies can use different ratios to understand the rate of returns on equity and invested capital in evaluating business financial health.
5. Make long-term business decisions
A balance sheet is a useful tool for businesses engaging in long-term financial planning.
Combined with the other financial statements (cash flow statement and income statement), a balance sheet is a useful tool for decision-making.
With continuous and recurring monitoring of the balance sheet, businesses can help you map growth opportunities and plan for the future with more confidence.
 |
|
It’s important to know what your asset and liability balances are in their original foreign currencies, but also in terms of what they’re worth in the company’s operating or home currency.
It’s also important to work with a company that minimizes bank charges and offers the most advantageous exchange rates to maximize the company’s bottom line.
However, just because someone owes you money doesn’t mean that you’re going to receive it in a timely fashion.
International money transfers have traditionally been costly and time-consuming, for both the sender and the receiver. This has meant a high barrier to international trade in the past.
If you can find a company that can move the money easily and quickly, and which can minimize the bank fees, this means that your foreign receivables are worth more in your home currency. And it also means that paying your foreign payables will cost you less!
| 💡 Did you know? |
|---|
| Make money management and currency conversion easier with the Wise Business multi-currency account. See your transactions and subscriptions all in one place. |
|---|

Keep your payments, withdrawals, and subscriptions in one place using your multi-currency account.
With the Wise Business account you’ll be able to see all your transactions in each currency your customers pay you, making cash flow management easier.
Plus you can limit your exposure to expensive conversion fees, making payments at the mid-market rate.
Using Wise, get account details such as IBAN, routing number, source code, and other local banking details for 10 currencies. You can make invoicing smarter by adding these details to invoice templates and get paid on time like a local.
Plus, this way you can offer customers to pay you in their own currency, making the whole process more convenient.
In addition, you can save up to 19x compared to PayPal on international transfers when you send money online with Wise.
Open your Wise Business account today
Sources
All sources checked 27 December 2021
*Please see terms of use and product availability for your region or visit Wise fees and pricing for the most up to date pricing and fee information.
This publication is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from Wise Payments Limited or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or guarantees, whether expressed or implied, that the content in the publication is accurate, complete or up to date.

Outsource to Romania with confidence. Discover the benefits, costs, and practical steps for US businesses.

In this US guide to buying commercial property in Singapore, navigate the process, costs, and unlock foreign investment opportunities with expert insights.

Discover the most secure and convenient online payment methods for your business.

Learn the essentials of how to invest in commercial property in the UK as a US investor.

Compare Mollie vs Stripe to find the best payment gateway for your business. Our guide covers fees, features, and integrations to help make the right choice.

Find out how to open an IBAN account with our step-by-step guide. Understand the requirements, benefits, and best practices.