Wise Business Pricing Explained (US)
Having trouble deciding which Wise Business account is best for your business? We’re breaking down the differences between the ‘Essential’ and ‘Advanced’...

When it comes to determining the financial health of a business, a question that comes up often is what an income statement is.
An income statement - also known as profit and loss statement - is one of the key financial statements analyzed, looking at a company's income in a given period. It helps you understand a company’s income versus its expenses to evaluate business performance.
| What goes in an income statement? | Definition¹ |
|---|---|
| Revenue | All of the money your business earns from selling its goods and services |
| Cost of Goods Sold | The true cost to produce and sell goods or services, including raw material and labor needed. |
| Operating Expenses | All expenses incurred to keep the business running as normal, such as rent. |
| Depreciation | Expenses that incur over time, such as the declining value of equipment and assets. |
| Gross Profit | The total profit your business earns, after subtracting the cost of goods. |
Get your free income statement template in a click
This article will look at how to prepare an income statement in 9 easy steps.
The first step is to add revenue figures for your reporting period.
Revenue can include sales from products and/or services sold.
It can also include any revenue earned through interest, sold assets, and other income streams your business might have.
Once all the revenue is added up, you’ll subtract returns, discounts, and other allowances to identify your net sales figure.
Net sales is the total of sales without deducting for operational expenses. It helps you better understand how much money the company is truly earning.
The next step in preparing an income statement is to include the Cost of Goods figures.
The cost of Goods includes both the raw material and labor needed to create and bring your product to market.
Cost of Goods can also include overhead directly related to production, such as factory expenses incurred.²
Once you’ve included your total revenue and figures for the Cost of Goods Sold, you’ll then have the calculation for gross profit.
Gross profit shows how much money your business has made after accounting for the costs to create the product itself.
It’s a key measure to understand business health and the overall profitability of the business.
Operating expenses are defined as any costs incurred to keep your business running normally.
Most businesses tend to have similar types of operating expenses such as marketing and advertising, wages, and rent. However, some businesses will have more operating expenses than others or have different ones.
For example, international businesses might have more operating expenses due to managing multiple locations and payroll compared to domestic businesses.
For this step, take some time to fully identify all operating expenses your business incurs to ensure you’re getting the full picture.
Manage your expenses and cash flow
with Wise Business
After entering all your operating expenses, you will have to calculate operating profit.
Operating profit refers to your business’ profits after deducting operating expenses. It shows how much money your business has to spend after paying its expenses but before interest or tax.
This measure is crucial to identify how high your profit margins are, and it’s a key measure of financial performance.
If your business has any sources of income that are not generated or related to its core services or products, it is included as other income.
This can include money earned from interest or from selling assets.³
The next step for preparing your income statement is to subtract tax expenses from profit (before tax).
Tax expenses can vary based on what country your business operates in and if you have multiple international locations.
It can be beneficial to get familiar with international taxes and business obligations, including treaties and other measures.
This is the last deduction you’ll need to make from your profits to understand profit and loss for your business.
Now that all the information is included for revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expense, and taxes, you should have a figure that shows your company’s net profit.
This is how much your business earns after deducting expenses, taxes, and interest. It shows how well your business is performing financially and whether it can retain profits after deductions.
It’s a key metric used to determine financial health and forecast how businesses might perform in the future.
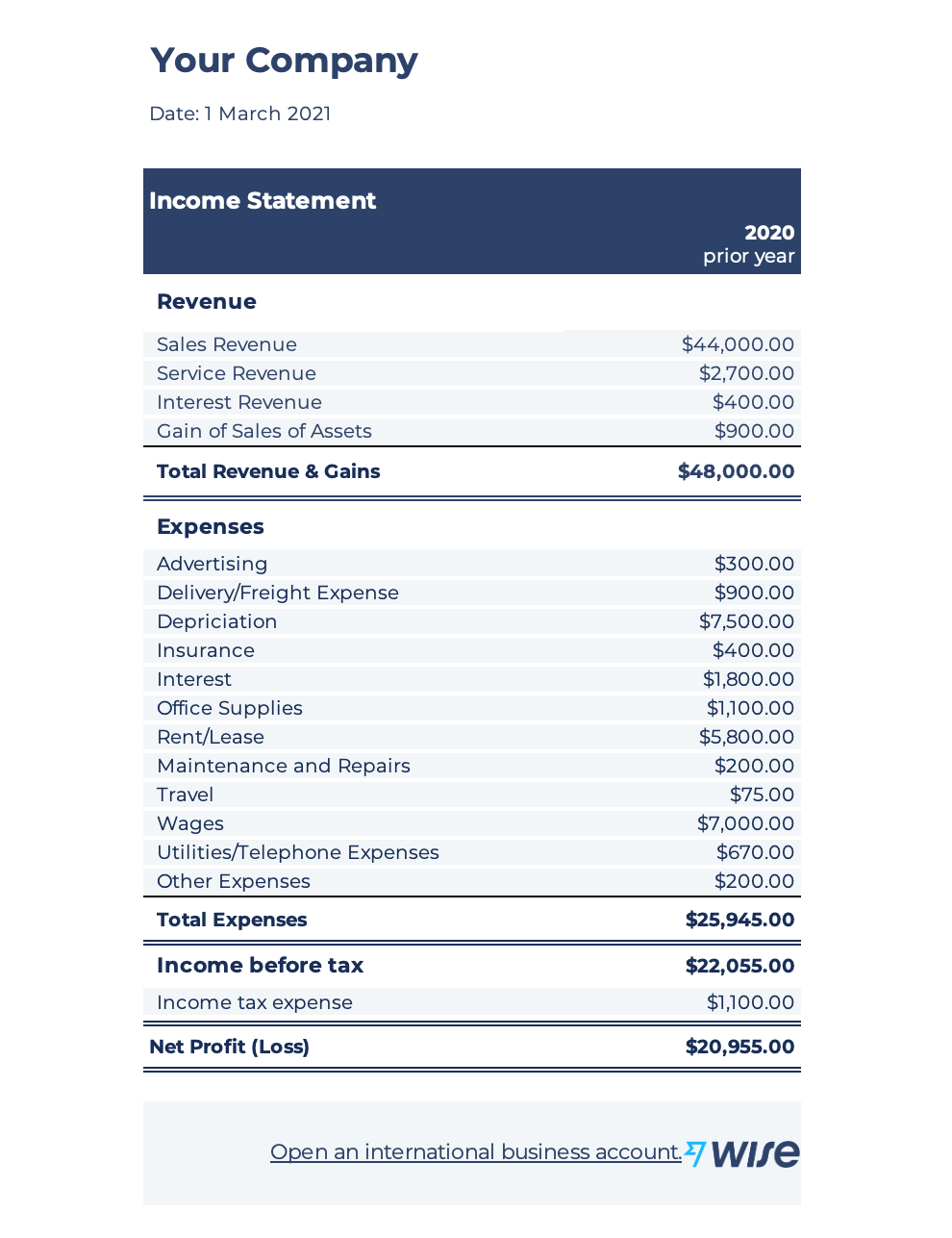
To help with the process, here is an example of an income statement. The first example below is a simple income statement to help you identify how profitable your business is versus how much it is spending.
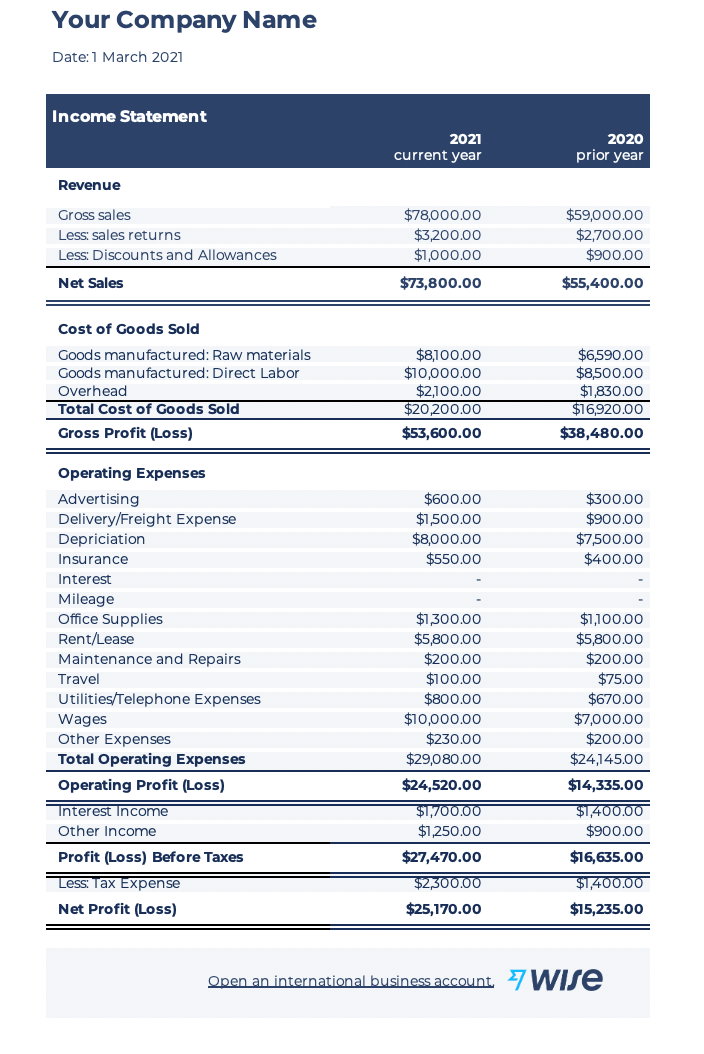
If you’d like a more comprehensive overview of a business, here is an example of an income statement that goes deeper.
In the comprehensive income statement example, the income statement is broken down into three areas: Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, and Operating Expense.
Always remember that income statements are an important part of financial analysis, but you should not evaluate them in isolation.
To fully determine the financial health of a business and its profitability, it is crucial to look at other financial statements, such as cash flow and balance sheet for a more well-rounded analysis of how your business is performing.
When we look at financial statements as a whole, income statements and balance sheets complement one another.
An income statement looks at a company’s profit and loss, and is used to understand how profitable a business is after it accounts for its expenses.
However, a balance sheet looks at how much a business is earning versus its liabilities to understand its total value of the company.⁴
One of the key differences between income statement vs balance sheet is timing.
The second difference is what the income statement includes versus the balance sheet.

With Wise, you can take control of your cash flow, manage invoices and gain more visibility on money management.
The Wise multi-currency account makes international payment management easier,by allowing you to handle all your transactions in one place, over 50 currencies.
Get account details -such as IBAN, sort code, routing number and more- in up to 10 currencies, and offer customers more flexibility by letting them pay you in their own currency.
Streamline money management with batch payments, and save up to 19x compared to PayPal* when you use Wise.
Open your Wise business account today
| *💡 Did you know? |
|---|
| Wise did some research, comparing their business prices to PayPal’s. The research was carried out between 6 January 2021 and 14 January 2021. |
|
All sources checked 11 November 2021
*Please see terms of use and product availability for your region or visit Wise fees and pricing for the most up to date pricing and fee information.
This publication is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from Wise Payments Limited or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or guarantees, whether expressed or implied, that the content in the publication is accurate, complete or up to date.

Having trouble deciding which Wise Business account is best for your business? We’re breaking down the differences between the ‘Essential’ and ‘Advanced’...

Compare Klarna vs. Affirm to help you decide which is a better fit for your business. Explore fees, features, products, and more.

Get a comprehensive review of Shopify Plus for global expansion, including key features, pricing, and best practices

Compare Quickbooks and Xero. We'll look at their features, costs, and what makes each one stand out. Find out the best fit for your business needs.

Discover the best corporate card options in fintech. Modern, flexible cards with advanced expense management and security features.

Explore Revolut Business integrations: connect your account with popular accounting and business software to automate workflows and save time.