Is Venmo Safe for Sellers? Tips, Risks, and Security
Is Venmo safe for sellers? Learn about the risks, payment protection policies, and best practices to protect your business.

Cash flow and revenue are absolutely essential for a business and its financial health, but it’s often easy to confuse the two. Both are important metrics for evaluating financial performance, but they tell different stories.
Having an understanding of what cash flow is, what revenue is, and how they are different can help when planning out financial decisions for a business.
This article will break down revenue vs. cash flow and the differences between the two.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Cash flow and revenue are two different metrics that measure how businesses generate and spend money.
Let’s take a look at the main aspects of cash flow and revenue and then at each one individually to better understand their role in business finance.
| Cash flow | Revenue | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflow and outflow of money as a business operates | Money earned through selling products and/or services |
| Position in the business | Looks at cash entering a business and leaving a business (two-way) | Looks at money entering a business (one-way) |
| Calculation | Adjusts net income through addition and subtraction of revenue, expense, and credit² |
|
| Participation in business health | Used to measure liquidity. Also used to monitor financial health and optimise costs based on spending. | Measuring income through sales, a major indication of the success of the business’ marketing |
In its simplest terms, cash flow refers to money the business generates and spends as a result of its normal operations.³
When a business has positive cash flow, it can suggest that it is in a good position to grow.
For example, with positive cash flow, stock buybacks are possible, the business can repay debts, explore growth opportunities, expand inventory, and more.
However, negative cash flow can suggest that the business needs to make changes in order for it to be profitable in the long run.
For example, if negative cash flow results from expansion and debt repayments, it means the business is investing in itself and should be more profitable in the future.
However, if negative cash flow has occurred because the business is incurring more expenses than income, it’s a sign of potential financial distress if not mitigated early.
A cash flow statement can help analyse cash flow for a business, making it a vital tool for financial performance.
Preparing a cash flow statement, businesses can monitor and manage cash flow by understanding the impact of expenses and revenue on cash.
Take control of your cash flow with
the Wise cash flow statement
A cash flow statement consists of different types of cash flow:
Operating cash flow refers to cash inflow and outflow generated by business operations. For example, it could include cross-currency supplier payments, payroll, office rent in multiple locations, etc.
Cash flow from investing activities refers to cash inflow and outflow generated through investments. That can include purchasing property and equipment needed for the business to grow, business acquisitions, purchase and sales of stocks and bonds, and more.
Cash flow from financing refers to inflow and outflow generated through activities such as issuances and/or repayments of equity, issuance and/or debt repayment, dividend payments, and other financing activities.
Revenue is essentially a measure of how much money a business makes through selling its products and services.⁴ On income statements, it might be referred to as sales, returns, or earnings.
Analyze your company performance,
with the Wise income statement
Revenue is a one-way figure - it does not look at inflow and outflow. It’s simply a measure of how much money is being generated as products and services are sold.
However, an important distinction to make is that revenue does not equal profit.
Profit can very much be negative and is referred to as a loss.
Revenue is simply the income coming into the business without other influences such as expenditure and profit.
Another important point to make about revenue is that it can vary depending on the nature of the organization.
For retail, it can be sales of goods and services.
For governments, it can be taxes and programs.
For charities, revenue comes in the form of donations and grants.
So although the sources of revenue will vary, the metric is ultimately looking at how much money is coming in.
While cash flow measures liquidity, revenue measures business sales.
When revenue is high, it could mean that a business is successful at marketing and generating sales.
In contrast, low revenue can mean that the business is marketing itself poorly or ineffectively, decreasing sales.
Revenue can be divided into operating and non-operating revenue (i.e., derived from secondary sources).
Accrued revenue refers to when businesses have earned revenue through a sale, but cash has not yet been received. The business recognizes the sale, but the customer has not paid as of yet.
For example, accrued revenue can refer to international sales to buyers where the sale has closed, but the customer has not yet been billed due to currency differences.
Unearned revenue is income the business receives that it has not generated.
Sources of unearned revenue can include payments from stocks, dividends and other international investments such as leaseholds that generate passive income for a business.
To help with understanding the difference between revenue and cash flow, you can use Wise templates to calculate the two for yourself.
For example, you can use the Wise income statement to calculate revenue and calculate cash flow using the cash flow statement template.
Below, you’ll see an example of an income statement, where revenue is listed at the top.
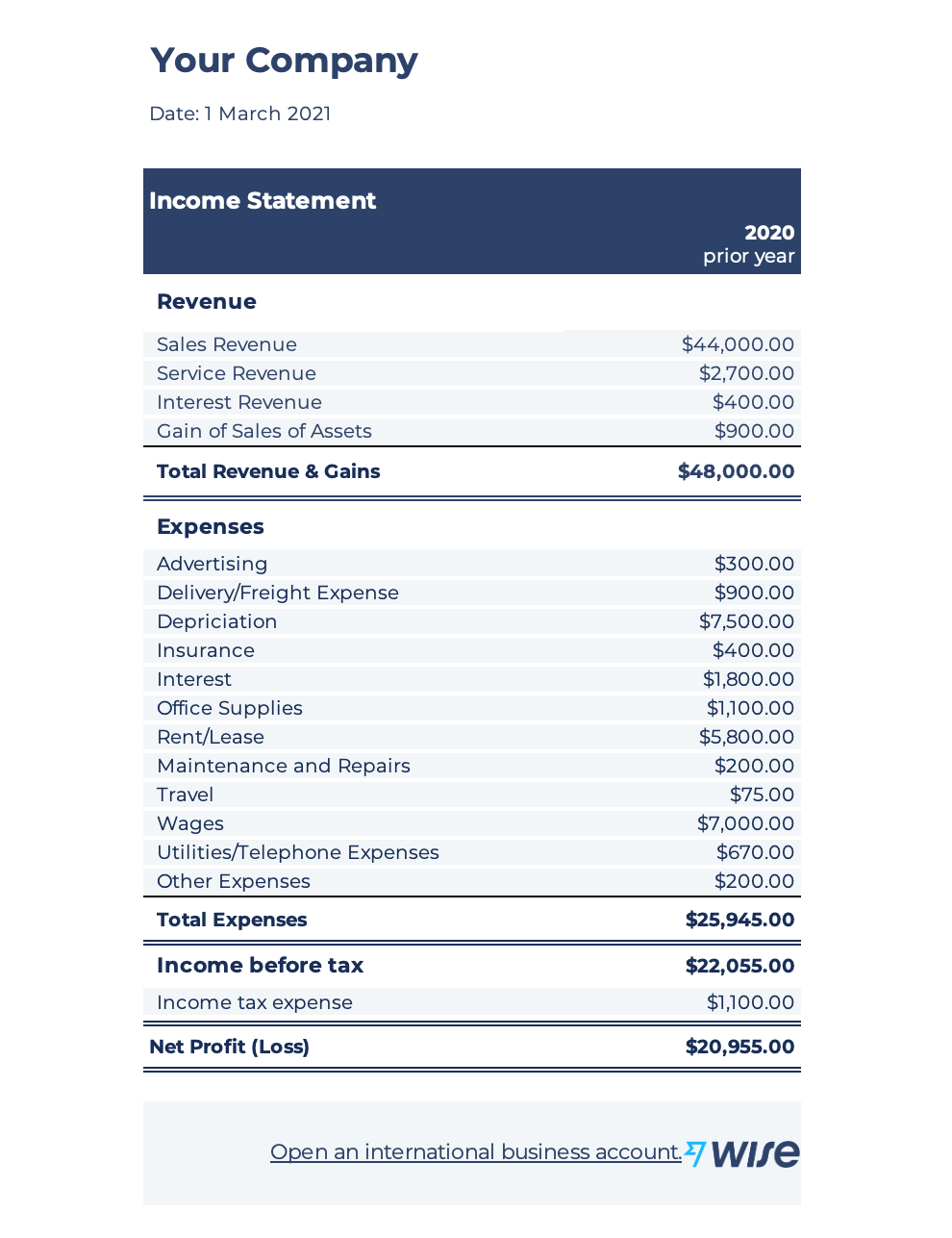
Now take a look at the cash flow statement. As you can see, inflow and outflow of different types of cash flow are listed.
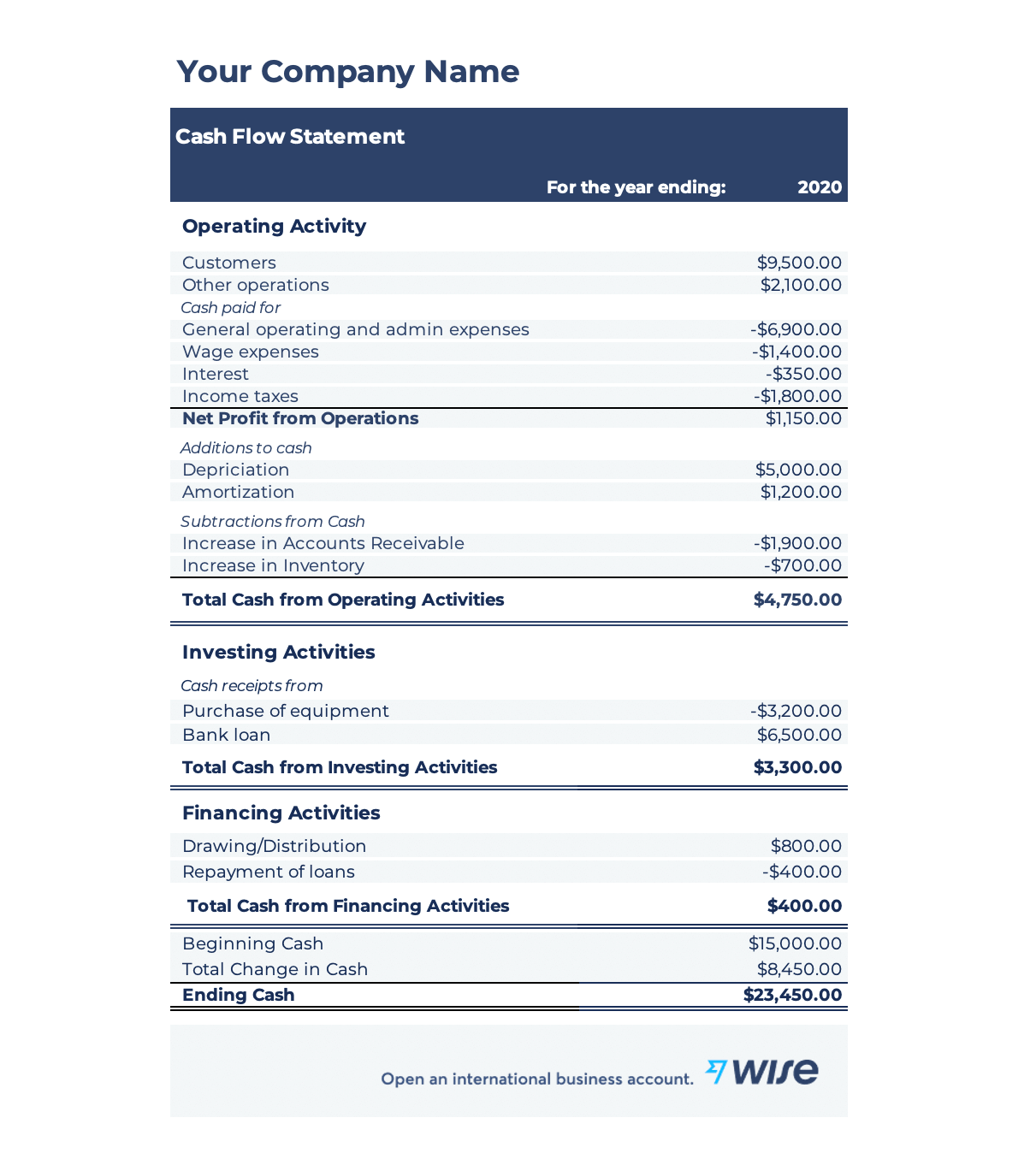
Revenue and cash flow are crucial metrics to understand business performance and with Wise, you get the visibility you need to take control of business finance.
Make money management easy. Check your account, move money, and manage up to 54 currencies with your Wise multi-currency account.
Send money with the mid-market rate and simple, transparent fees that are clear and upfront every time, so you’ll know the exact amount you have to pay.
Open your business account today 💼
Sources:All sources checked 12 October 2021
*Please see terms of use and product availability for your region or visit Wise fees and pricing for the most up to date pricing and fee information.
This publication is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from Wise Payments Limited or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or guarantees, whether expressed or implied, that the content in the publication is accurate, complete or up to date.

Is Venmo safe for sellers? Learn about the risks, payment protection policies, and best practices to protect your business.

Find out the benefits of paying vendors via ACH (Automated Clearing House) for secure, low-cost, and reliable electronic funds transfers.

Looking for a business account Malta? Compare top banks and fintech options to manage your finances in this EU island nation.

Explore embedded payments and how integrating payment functionality directly into your software can enhance user experience and streamline transactions.

Tips and methods on how to pay vendors with a credit card, including options for businesses to manage working capital and earn rewards.

Learn whether an independent contractor needs an LLC. Explore the benefits, and how to decide if it is right for your business.